- Have any questions?
- 085913 90567
- drgeorgechestdiseases@gmail.com
Smoking and Lung Cancer: Understanding the Deadly Connection
Lung Cancer: Symptoms and Treatment Plan
December 23, 2024
Is Throat Cancer the Same as Esophagus Cancer?
January 6, 2025Understanding Lung Cancer
When we hear about lung cancer, most of us instantly think of smoking. And for good reason—smoking is responsible for 80% of lung cancer cases. But did you know that lung cancer is the fourth most common cancer in India? It’s a disease that can often be prevented but remains deadly due to late detection.
Dr. George Karimundackal, a leading thoracic surgeon in Mumbai, points out that lung cancer is prevalent among smokers. The longer and heavier the smoking, the higher the risk. But even non-smokers aren’t entirely safe—those exposed to secondhand smoke also face serious risks.
So, what exactly is lung cancer? In simple terms, it is when lung cells start growing uncontrollably. These abnormal cells can form tumors, affect breathing, and even spread to other parts of the body. The scary part? Lung cancer often doesn’t show clear symptoms until it is in the advanced stages.
Now, let’s talk about the types of lung cancer:
- Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common lung cancer in smokers, making up about 85% of all cases. It generally grows slower and is often found in smokers.
- Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is less common but much more aggressive. It tends to grow and spread faster, making early detection critical. This type is also linked to smoking.
Scroll down to learn how smoking plays a significant role in lung cancer development.
How Does Smoking Cause Cancer?
Have you ever wondered how smoking causes the disease? Let’s break it down.
Harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke
Tobacco smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are toxic. Some of the most harmful ones include:
- Carcinogens: Chemicals like tar, formaldehyde, and benzene are known to directly cause cancer by damaging DNA in the lung cells. Once DNA is damaged, cells can grow abnormally, leading to cancer.
- Nicotine: While primarily known for causing addiction, nicotine also plays a role in promoting cancer growth by speeding up cell division.
These harmful chemicals don’t just stay in your lungs—they travel throughout your body, causing damage to many organs.
Mechanisms of cancer development
When you inhale tobacco smoke, the chemicals start to damage your lung cells almost immediately. Over time, this damage adds up. The body’s ability to repair the damage is overwhelmed, leading to mutations in the DNA. These mutations cause lung cells to grow uncontrollably, forming tumors.
The more you smoke, the more damage is done. Smoking also weakens the immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off abnormal cell growth. Even if you quit smoking, the damage can persist for years, continuing to increase your risk of lung cancer.
Learn how smoking and lung cancer are linked. Take steps to protect your health by consulting a lung specialist.
Moving forward, let’s check out what can increase your risk of lung cancer.
Risk Factors Enhancing Lung Cancer Development
Risk factors that can increase your chances of developing the disease are as follows:
Duration and intensity of smoking

The longer you smoke, the higher your risk. Dr. George Karimundackal, a lung cancer specialist in Mumbai explains that even if you stop smoking today, your lungs don’t return to normal right away. In fact, after 10 years of quitting, your risk of lung cancer is still 50% higher than that of a non-smoker.
If you have been smoking for 20 to 30 years, it could take over three decades for your lungs to recover fully and for your risk to drop to that of a non-smoker. The intensity of smoking, or how many cigarettes you smoke a day, also plays a role—the more you smoke, the more damage is done.
Secondhand smoke exposure

You don’t have to be a smoker to be at risk. Secondhand smoke, or breathing in smoke from someone else’s cigarettes, can also cause lung cancer. Those living with smokers or spending time around them regularly are exposed to the same harmful chemicals. Dr. George highlights that even passive smokers carry a significant risk of developing lung cancer.
Other Factors
Other risk factors, like exposure to harmful substances (asbestos, radon) and a family history of lung cancer, can also increase your chances. But smoking and secondhand smoke exposure remain the biggest threats.
Did you know that spotting the early signs could save your life?
Symptoms and Early Detection
Lung cancer is dangerous because it often shows no symptoms in its early stages. That’s why being aware of the warning signs and focusing on early detection can make a huge difference.
Common Symptoms

Here are some of the symptoms to look out for:
- Persistent cough that doesn’t go away or worsens over time.
- Pain in the chest that gets worse with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing, especially if it is new or getting worse.
- Coughing up blood should not be ignored.
- Feeling unusually tired or weak without any apparent reason.
- Unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms might not always point to lung cancer, but if they persist, it’s crucial to see a doctor.
Importance of early detection
Dr. George Karimundackal, a lungs specialist in Mumbai, stresses that early detection is vital to improving the chances of successful treatment. Lung cancer often progresses silently, and by the time symptoms become noticeable, the cancer may have spread. Regular screenings, especially for high-risk individuals like long-time smokers, can catch the disease early when it is easier to treat.
Low-dose CT scans are one of the most effective tools for early detection in high-risk groups. These scans can identify small tumors that may not be causing any symptoms yet. If caught early, lung cancer treatments are more effective, and survival rates improve significantly.
Find out how cigarette cause lung cancer and how early detection can help by consulting with a lung cancer specialist today.
Are you facing lung cancer? Let’s explore how each treatment can make a difference.
Treatment Options
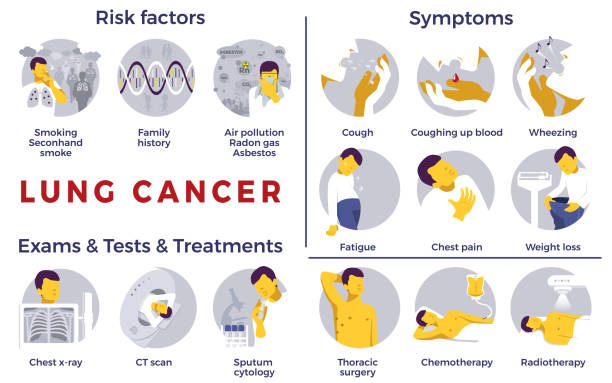
Lung cancer treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health. Early detection provides more effective options. Here are the main treatments:
- Surgery: Removes the tumor and surrounding lung tissue, usually for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It is used when surgery isn’t an option or alongside surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s often used for small cell lung cancer (SCLC) or advanced NSCLC and can follow surgery to reduce recurrence risk.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific changes in cancer cells, often used for advanced NSCLC to slow growth.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer, especially in advanced stages when other treatments aren’t working.
Each patient’s treatment plan is personalized to ensure the best results while maintaining quality of life.
Want to lower your risk of lung cancer? Start here…
Prevention Strategies

Preventing lung cancer starts with reducing the risk factors, such as:
- Quit smoking: The most effective way to prevent lung cancer. Even long-time smokers benefit from quitting, as it reduces the risk over time.
- Avoid secondhand smoke: If you live or work around smokers, limit your exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Test for radon: Radon is a natural gas that can increase lung cancer risk. Testing your home for radon levels, especially in areas with known risks, can help.
- Follow workplace safety guidelines: If you work in industries that expose you to harmful chemicals (like asbestos), ensure you follow safety protocols to minimize exposure.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables and regular exercise can strengthen the immune system and reduce cancer risk.
Now, let’s explore the promising research and what the future holds for lung cancer care.
Current Research and Future Directions
Lung cancer research is continuously evolving, offering new hope for patients. Key areas of focus include:
- Better early detection: Ongoing studies aim to improve low-dose CT scans and find less invasive tests, like blood tests (liquid biopsies), to catch lung cancer early.
- Genetic testing: Researchers are exploring how genetic mutations affect cancer development and how personalized treatments can target these changes.
- Prevention programs: Public health initiatives aim to reduce smoking rates and raise awareness about secondhand smoke and other environmental risks.
Advancements in Treatment
Recent advancements in lung cancer treatment are giving patients more options and better outcomes:
- Immunotherapy: New drugs are helping the body’s immune system better recognize and attack cancer cells, offering hope to patients in advanced stages.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that focus on specific genetic mutations in cancer cells are improving outcomes, particularly for those with non-small cell lung cancer.
- Minimally invasive surgeries: Techniques like video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and robotic surgery allow for faster recovery and fewer complications in early-stage lung cancer.
Concerned about lung cancer because of smoking? Book an appointment with a thoracic surgeon to explore ways to lower your risk.
Conclusion
Lung cancer remains one of the most severe health threats, primarily because of smoking. The good news is that prevention is possible by quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, and staying informed. With advances in early detection and treatment, patients have more hope than ever. By taking steps now, we can reduce the impact of lung cancer and save lives.
Reference
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4080902/https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/smoking-and-cancer/how-does-smoking-cause-cancer
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes lung cancer in non-smokers?
Lung cancer in non-smokers can be caused by several factors, including:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Air pollution
- Radon gas
- Asbestos
- Genetic mutations
What does smoking do to your lungs?
Smoking reduces lung function, causes long-term damage, and increases the risk of severe diseases like lung cancer and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
What percent of smokers develop lung cancer?
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. While the exact percentage varies, a significant portion of lifelong smokers develop the disease. The risk increases with the duration and intensity of smoking.
Do tobacco cause cancer?
Yes, tobacco is a major cause of cancer. Smoking tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and smokeless tobacco, significantly increases the risk of developing various types of cancer, such as lung cancer, oral cancer, throat cancer, esophageal cancer, pancreatic cancer, and many others.
Can you get lung cancer without smoking?
Yes, you can get lung cancer without smoking. Around 10-20% of people who develop lung cancer have never smoked.
Does second hand smoking cause cancer?
Secondhand smoke can cause cancer. Inhaling smoke from someone else’s cigarette exposes you to the same harmful chemicals as smoking directly. Long-term exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk of lung cancer by 20-30% in non-smokers.
When you quit smoking, what happens to your lungs?
When you quit smoking, your lungs start healing. Within days, oxygen levels improve, and within months, the cilia (tiny hairs) recover, helping clear mucus. Over time, lung function improves; after ten years, your risk of lung cancer is reduced by half.
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.