- Have any questions?
- 085913 90567
- drgeorgechestdiseases@gmail.com
Lung Cancer from Air Pollution

Can You Get Lung Cancer Without Smoking?
February 14, 2025
Effect of Smoking on the Lungs: Understanding the consequences
March 13, 2025Introduction: The Air We Breathe, The Risk We Face
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest diseases worldwide, claiming millions of lives every year. It can affect anyone, and its impact on health, families, and economies is profound. According to the World Health Organization, lung cancer accounts for approximately 2.2 million new cases annually, making it a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally.
“Air pollution has become an unavoidable reality of urban life, and its role in lung cancer cannot be ignored,” says Dr. George Karimundackal, a seasoned thoracic surgeon in Mumbai. “The surge in industrial activities, vehicular emissions, and environmental degradation has led to a sharp rise in lung cancer cases, particularly in metropolitan areas.”
This blog explores the connection between air pollution and cancer, identifying harmful pollutants, understanding their impact, recognizing at-risk individuals, and discussing preventive measures.
What Pollutants in the Air Cause Lung Cancer?
Polluted air contains various carcinogens that increase lung cancer risk. Some of the most harmful pollutants include:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10) – Fine particles that penetrate deep into lung tissues.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) – A toxic gas emitted by vehicles and industrial processes.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) – Released from burning fossil fuels.
- Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) – Formed from burning organic materials.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) – Found in industrial emissions and household chemicals.
- Ozone (O3) – A secondary pollutant formed by chemical reactions in the atmosphere.
Are you concerned about your exposure to polluted air? Consult a trusted Lung Cancer Specialist for expert guidance on minimizing risks.
But how do these pollutants contribute to lung cancer? Let’s break it down.
Understanding How Air Pollution Triggers Lung Cancer
Exposure to air pollution damages lung tissues and increases the likelihood of cancerous changes. Here’s how:
- Inflammation and Cellular Damage – Pollutants cause chronic inflammation, leading to DNA mutations.
- Oxidative Stress – Harmful compounds in polluted air generate free radicals, which damage healthy lung cells.
- Disrupted Immune Response – The immune system struggles to clear toxic particles, allowing cancerous cells to grow.
- Long-Term Exposure Risks – Prolonged exposure to toxic air leads to cumulative damage, raising lung cancer risk significantly.
While smoking remains the leading cause, poor air quality is emerging as a major contributor to lung malignancies.
Who is Most at Risk?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing lung cancer due to air pollution, including:
- People Living in Urban and Industrial Areas – Higher exposure to vehicular and industrial emissions.
- Elderly Individuals – Reduced lung capacity and weakened immunity.
- Children and Pregnant Women – Developing lungs are highly sensitive to pollutants.
- People with Pre-existing Respiratory Conditions – Asthma and COPD patients face heightened risks.
- Outdoor and Industrial Workers – Prolonged exposure to high-pollution environments.
“Lung cancer cases are increasing in densely populated cities due to prolonged exposure to harmful pollutants,” notes Dr. George Karimundackal, a trusted robotic thoracic surgeon in Mumbai. “Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable as their lungs are more sensitive to toxins. People working in high-emission industries should take extra precautions to minimize exposure.”
Fortunately, there are ways to reduce your risk. Let’s explore them.
Reducing Your Risk of Lung Cancer from Air Pollution
Protecting yourself from harmful pollutants can significantly lower lung cancer risk:
- Monitor Air Quality – Use air quality apps to stay informed and avoid high-pollution days.
- Use Air Purifiers – Invest in HEPA filters for cleaner indoor air.
- Wear Protective Masks – N95 masks can reduce pollutant inhalation in heavily polluted areas.
- Plant More Greenery – Trees and plants act as natural air filters.
- Reduce Fossil Fuel Usage – Opt for cleaner transportation and energy sources.
Worried about the long-term effects of air pollution? Consult an acclaimed Lung Cancer Specialist to assess your risks and explore preventive measures.
Early detection is key to better outcomes. Let’s look at the symptoms.
Lung Cancer Symptoms and Early Detection
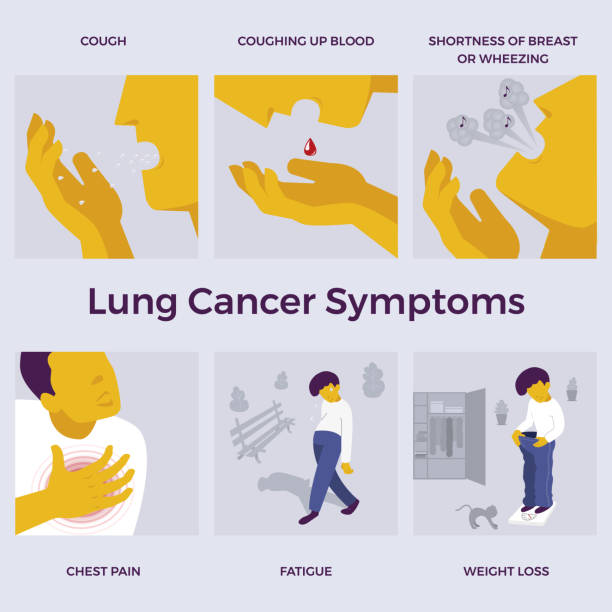
Recognizing lung cancer symptoms early can improve treatment success rates. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent Cough – A lingering cough that worsens over time.
- Shortness of Breath – Difficulty breathing even during mild activities.
- Chest Pain – Discomfort that worsens with deep breaths or coughing.
- Unexplained Weight Loss – Rapid, unintentional weight loss.
- Fatigue and Weakness – A persistent feeling of exhaustion.
“Many patients ignore mild respiratory symptoms, delaying diagnosis,” warns Dr. George Karimundackal, an esteemed thoracic surgeon in Mumbai. “Persistent cough and breathlessness should never be overlooked. Early screening through low-dose CT scans can significantly improve survival rates.”
Conclusion: Breathing Easier, Living Longer
Lung cancer from air pollution is an emerging public health crisis. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and taking preventive steps can make a significant difference. Seeking expert medical guidance is essential for timely intervention and better outcomes.
“While air pollution remains a challenge, early intervention and lifestyle changes can help mitigate its risks,” emphasizes Dr. George Karimundackal, a thoracic specialist renowned for effective tracheal surgery in Mumbai. “Every individual must take proactive steps to protect their lung health. Regular check-ups and awareness are the first lines of defense against pollution-induced lung diseases.”
Do you have concerns about lung health? Seek expert advice from a renowned Lung Cancer Specialist for a comprehensive assessment.
Still have questions? Here are some answers to common concerns.
FAQs
Is increasing air pollution the cause of lung cancer?
Studies confirm that prolonged exposure to air pollution increases lung cancer risk. Fine particulate matter and toxic chemicals in polluted air damage lung cells, leading to mutations and uncontrolled cell growth.
What are the lung diseases caused by air pollution?
Air pollution can cause various respiratory diseases, including chronic bronchitis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. It also exacerbates existing lung conditions, leading to severe complications.
Which air pollutants can cause cancer in humans?
Several air pollutants are classified as carcinogens, including particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Long-term exposure to these pollutants significantly increases cancer risk.
Reference Links:
https://www.lung.org/research/sota/health-risks
https://www.uicc.org/what-we-do/thematic-areas/cancer-and-air-pollution
Disclaimer: The information shared in this content is for educational purposes only and not for promotional use.

