- Have any questions?
- 085913 90567
- drgeorgechestdiseases@gmail.com
Empyema vs Pleural Effusion: What’s the Difference?
What to Do If You Are Anxious About Lung Cancer
January 11, 2025
Can You Get Lung Cancer Without Smoking?
February 14, 2025What is Pleural Effusion?
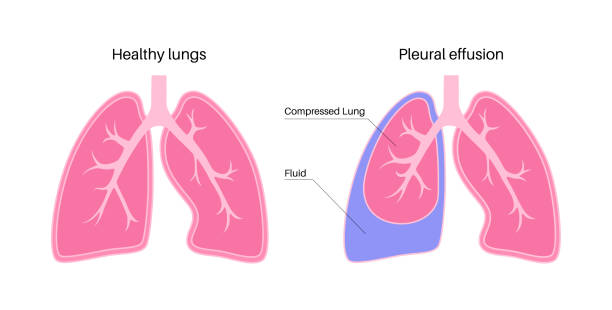
Pleural effusion occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the pleural space, a thin layer between the lungs and the chest wall. This buildup can restrict lung expansion, making breathing more difficult. Often, it signals an underlying condition rather than being a disease on its own.
Causes of Pleural Effusion
Several factors can lead to pleural effusion, including:
- Heart Conditions: Congestive heart failure is a common cause due to fluid retention.
- Infections: Pneumonia and other lung infections may trigger fluid accumulation.
- Cancer: Lung or breast cancer can spread to the pleura and cause effusion.
- Liver or Kidney Disorders: Conditions causing fluid imbalance can lead to pleural effusion.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A clot in the lungs can contribute to effusion.
Types of Pleural Effusion
- Transudative Effusion: Caused by systemic conditions like heart failure or liver disease, involving low-protein fluid.
- Exudative Effusion: Typically results from infections or malignancies, with protein-rich fluid.
Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
Symptoms depend on the amount of fluid and the underlying cause but may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially during deep breaths
- Persistent cough
- Fever and chills (if infection-related)
Now, let’s learn about empyema.
What is Empyema?

Empyema is a serious condition where pus collects in the pleural cavity, often following pneumonia or other lung infections. Left untreated, empyema can lead to scarring, reduced lung function, or severe systemic infections.
Causes of Empyema
Common causes of empyema include:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: The leading cause, involving pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Post-Surgical or Traumatic Infections: Infections from chest surgery or injury.
- Underlying Diseases: Tuberculosis or lung abscesses can progress to empyema.
Types of Empyema
- Acute Empyema: Early-stage infection with liquid pus accumulation.
- Chronic Empyema: Long-standing infection that results in thickened pleura and fibrous tissue formation.
Symptoms of Empyema
Empyema symptoms are often more severe than those of pleural effusion, including:
- High fever and chills
- Intense chest pain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Cough with foul-smelling sputum
- Difficulty breathing
Protect your respiratory health. Reach out to a lung doctor today for expert advice.
Still confused between the two? This table makes it simple!
Empyema vs Pleural Effusion: Key Differences

| Aspect | Pleural Effusion | Empyema |
| Cause | Fluid due to systemic or local factors | Pus from an infection in the pleura |
| Fluid Composition | Transudate or exudate | Pus |
| Symptoms | Mild to moderate respiratory distress | Severe infection symptoms |
| Treatment | May resolve with drainage or medication | Requires antibiotics, drainage and sometimes surgery |
How do doctors pinpoint the problem? Let’s explore.
Diagnosis of Pleural Effusion and Empyema
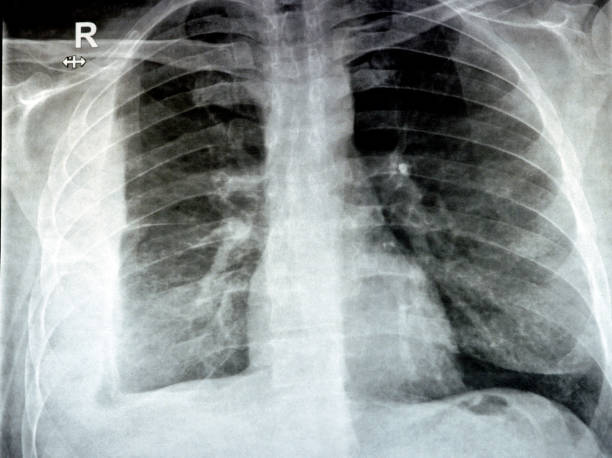
Accurate diagnosis is vital for proper treatment. Diagnostic tools include:
- Chest X-Ray: Reveals fluid or pus in the pleural cavity.
- Ultrasound or CT scan: Provides detailed imaging for better evaluation.
- Thoracentesis: A needle extracts fluid or pus for laboratory analysis.
- Blood Tests: Helps identify infections and inflammation.
What are the treatment options? Here’s what to expect
Treatment of Pleural Effusion and Empyema

Treating Pleural Effusion
- Medications: Diuretics for fluid control or antibiotics for infections.
- Thoracentesis: Fluid is drained to relieve symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions: Severe or recurring cases may require Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS) or a thoracotomy to remove excess fluid or address underlying causes.
Treating Empyema
- Antibiotics: Target the bacteria causing the infection.
- Chest Tube Drainage: A tube removes pus from the pleural cavity.
- Advanced Surgical Options: In later stages, procedures like VATS, thoracotomy, or surgical decortication may be necessary to remove thickened or fibrous pleural tissue.
Schedule a consultation with a thoracic surgeon to discuss advanced treatment options for pleural conditions.
Check out the ways in which these conditions can be prevented.
Prevention of Pleural Effusion and Empyema

- Timely Treatment of Infections: Address respiratory illnesses promptly.
- Vaccination: Protect against flu and pneumonia-causing bacteria.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Quit smoking and maintain good lung health.
- Routine Checkups: Especially important for those with chronic conditions like heart or lung disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between empyema vs pleural effusion is essential for timely and effective treatment. While pleural effusion is often linked to systemic conditions, empyema represents a more severe, localized infection requiring specialized care.
Dr. George Karimundackal, a trusted expert in thoracic surgery, underscores the importance of customized treatment. His expertise in advanced procedures like VATS and decortication ensures patients receive the best possible care for even the most challenging cases.
If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent chest pain or breathing difficulties, don’t wait—consult an expert today.
Reference
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3140254
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a dry cough and a cough with phlegm?
A dry cough doesn’t produce mucus, while a phlegm-producing cough indicates infection or inflammation.
2. What are the early warning signs of lung cancer?
Persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, chest pain, and coughing up blood are early signs.
3. Can anxiety cause chest pain?
Yes, anxiety can cause chest pain due to hyperventilation or muscle tension.
4. What are the risk factors for developing pneumonia?
Age, smoking, chronic illnesses, and weakened immunity are key risk factors.
5. How is tuberculosis treated?
Tuberculosis is treated with a combination of antibiotics for at least six months.
6. What is the best way to prevent the spread of flu?
Vaccination, hand hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are essential measures.