- Have any questions?
- 085913 90567
- drgeorgechestdiseases@gmail.com
Difference between Emphysema and Empyema
Is lung cancer hereditary?
July 15, 2025
Advances in Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: VATS vs RATS
August 13, 2025Lung diseases are a growing health concern worldwide, affecting millions annually. The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies respiratory diseases, such as lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia, as leading causes of illness. In India, factors like air pollution, smoking, and genetics are contributing to the rise in these diseases. One of the conditions that often confuse patients is emphysema, a form of COPD, and empyema, an infection in the pleural cavity.
Dr. George Karimundackal, a distinguished thoracic surgeon in Mumbai, emphasizes,
“Understanding the difference between emphysema and empyema is vital for tailoring the right care plan. While they may present with similar respiratory symptoms, their causes, progression, and treatments differ significantly.”
With over 15 years of experience in thoracic surgery, Dr. Karimundackal specializes in diagnosing and treating complex lung conditions. His expertise ensures that patients receive accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans, improving outcomes and quality of life.
Now, let’s discuss about emphysema in detail and how it impacts your lungs over time.
What Is Emphysema?
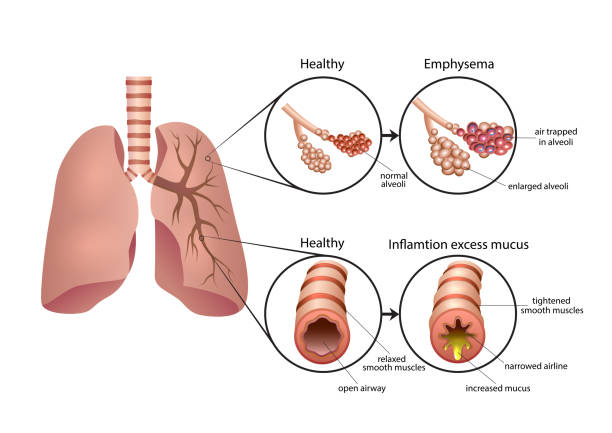
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition and a type of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It primarily damages the alveoli—the tiny air sacs in your lungs responsible for exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide. Over time, the inner walls of the alveoli weaken and may rupture, resulting in larger air spaces instead of many small ones. This reduces the surface area available for gas exchange, leading to shortness of breath and a persistent feeling of fatigue. Since the damage to the lungs is irreversible, early detection and proper management are essential for maintaining quality of life.
Let’s explore empyema and see how it differs from chronic lung conditions.
What Is Empyema?
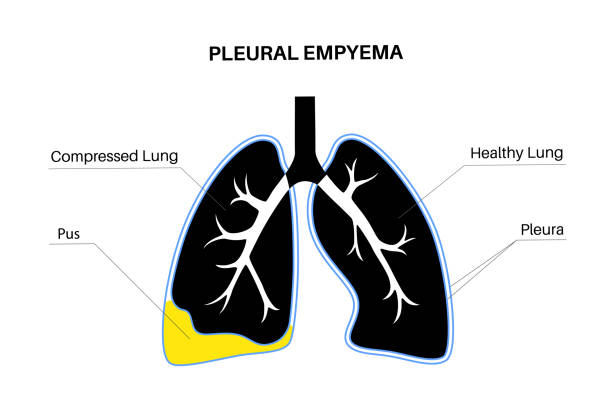
Empyema refers to the accumulation of pus in the pleural space, the area between the lungs and the chest wall. This condition typically arises as a complication of pneumonia but can also result from chest surgery, trauma, or infections spreading from other parts of the body.
The presence of pus in the pleural space leads to inflammation and impaired lung function. Without prompt treatment, empyema can lead to severe complications, including sepsis and lung scarring.
Let’s break it down and compare these two conditions side by side.
Emphysema vs Empyema: Key Differences
Though both emphysema and empyema are the conditions of the lungs, they differ fundamentally in their etiology, course, and management. A clear contrast is given below to know the difference between emphysema and empyema:
| Aspect | Emphysema | Empyema |
| Nature | Progressive and non-infectious; part of COPD. | Acute and infectious; often a complication of pneumonia. |
| Cause | Mainly caused by smoking, air pollution, or genetic factors. | Typically caused by bacterial infections after pneumonia or chest surgery. |
| Symptoms | Gradual shortness of breath, chronic cough, wheezing, and fatigue. | Sudden chest pain, high fever, cough, and difficulty breathing. |
| Treatment Focus | Managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. | Removing infection and draining pus from the pleural cavity. |
| Chronic or Acute? | Chronic condition requiring long-term management. | Acute condition requiring immediate intervention. |
| Contagious? | No, emphysema is not contagious. | Empyema itself isn’t contagious, but the underlying infections may be. |
Now, let’s talk about the tests and scans that identify these lung conditions
Diagnostic Methods
Correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. This is how doctors differentiate between emphysema and empyema through special tests and procedures:
Diagnostic Tools for Emphysema
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Measure lung capacity and airflow to detect airflow obstruction, a hallmark of emphysema.
- Chest X-ray or CT Scan: Visualizes hyperinflated lungs and damaged alveoli, confirming structural lung changes.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test: Assesses oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood to check how well the lungs are functioning.
- Oximetry: A simple, painless test to calculate blood oxygen level estimates.
Diagnostic Tools for Empyema
- Chest X-ray:
Demonstrates fluid buildup in the pleural space that usually presents as opaque regions.
- CT Scan:
Provides detailed images to assess the degree of infection and identify pus pockets.
- Ultrasound:
Aids in drainage of fluid and aids in determining the type of pleural fluid (free-flowing or loculated).
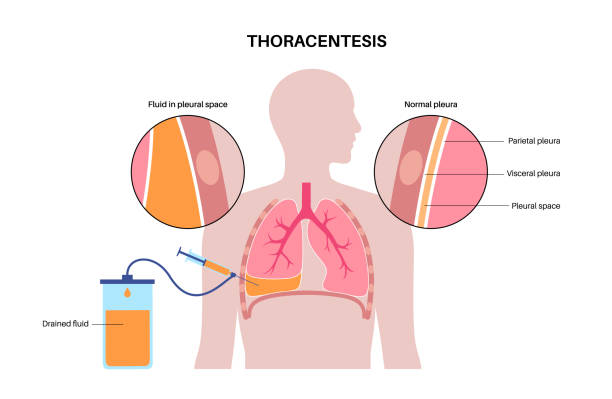
- Thoracentesis (Pleural Tap):
Involves aspirating fluid from the pleural space for laboratory testing to detect infection and guide management.
Want clarity on your symptoms in the lungs? Get connected with an expert skilled in advanced diagnostic care and personalized service.
Let’s discuss the various treatment choices for emphysema and empyema.
Treatment Approaches
Effective treatment not only relieves symptoms but also enhances long-term health outcomes. Below is a rundown of the treatment approaches employed in managing both conditions:
Emphysema Treatment Options
- Smoking Cessation:
The most important step; giving up smoking can greatly retard disease development and enhance lung function.
- Bronchodilators:
Medications (inhalers) that relax airway muscles to improve breathing.

- Inhaled Corticosteroids:
Reduce airway inflammation and help manage flare-ups.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation:
A structured program combining physical exercises, education, and breathing strategies to enhance lung capacity and quality of life.
- Oxygen Therapy:
Prescribed when blood oxygen levels are low; it improves energy levels and overall comfort.
- Vaccinations:
Prevent respiratory infections like influenza and pneumococcal pneumonia, which can worsen emphysema.
- Surgical Interventions:
In severe cases, lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) or lung transplantation may be considered.
Empyema Treatment Options
- Antibiotic Therapy:
IV or oral antibiotics depending on the particular bacteria present in pleural fluid culture.
- Thoracentesis:
A least invasive way to drain infected pleural fluid through the insertion of a needle.
- Chest Tube Drainage:
A tube is placed to drain pus from the pleural space continuously and reduce pressure on the lungs.
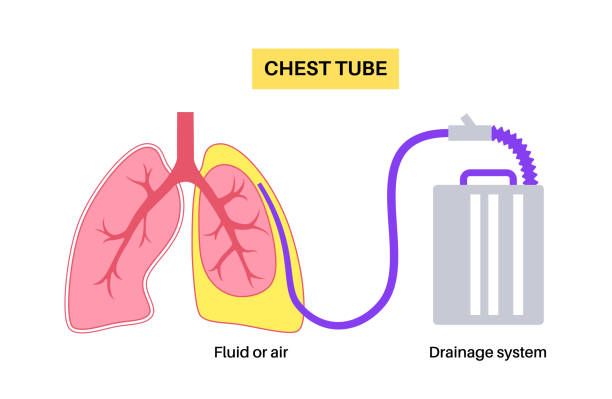
- Intrapleural Fibrinolytic Therapy:
Enzymes are injected into the pleural space to break down thick pus and improve drainage.
- Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS):
A minimally invasive surgical method to remove infected tissue and drain fluid when other methods fail.
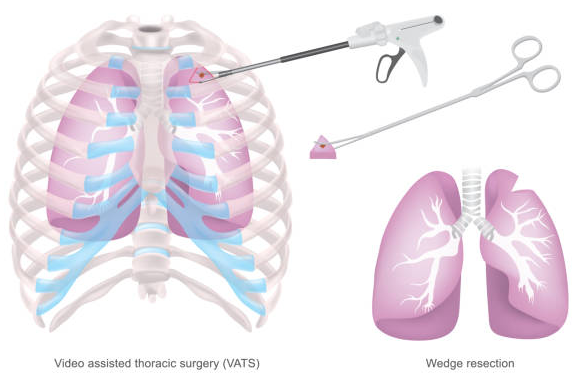
- Open Decortication Surgery:
Needed in severe cases when thick fibrous layers need to be excised from the lung surface so that it expands normally.
Can you have both conditions simultaneously? Let’s delve into this complex situation and explore its implications for patients.
Can You Have Both Conditions?
While emphysema and empyema are distinct conditions, a patient can experience both simultaneously, especially if underlying risk factors are present. For instance, a person with emphysema (a form of COPD) is more susceptible to infections like pneumonia, which can lead to empyema.
The coexistence of these conditions complicates treatment and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Managing the chronic aspects of emphysema while addressing the acute infection of empyema necessitates careful coordination between pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, and infectious disease specialists.
Early detection and integrated care are crucial for improving outcomes and reducing complications in patients with both conditions.
Unsure when to seek help for your symptoms? Let’s discuss the warning signs that indicate a doctor’s visit is necessary.
When to See a Doctor
Timely medical care is essential when suffering from:
- Recurring or increasing shortness of breath.
- Chest pain, particularly with deep breathing.
- Unexplained fever or chills.
- Chronic cough with sputum.
- Fatigue or unexplained weight loss.
Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between emphysema and empyema is vital for timely intervention. With accurate diagnosis and expert care from professionals like Dr. George Karimundackal, both conditions can be managed effectively.
With years of hands-on experience, Dr. Karimundackal helps patients with complex lung diseases lead a better quality of life by offering advanced treatments tailored to their specific conditions.
Don’t overlook respiratory symptoms. Contact an experienced specialist for proper evaluation and customized care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can emphysema turn into empyema?
No, emphysema does not specifically convert to empyema. However, individuals with emphysema are more prone to infections like pneumonia, which can lead to empyema.
Q2: Is empyema life-threatening?
Yes, empyema can be life-threatening if not treated promptly, as the infection can spread and lead to complications like sepsis or lung damage.
Q3: Can emphysema be reversed?
Emphysema cannot be reversed, but its progression can be slowed with proper treatment, lifestyle changes, and by avoiding lung irritants like smoking.
Q4: How long does empyema take to heal?
Empyema typically takes several weeks to a few months to heal, depending on the severity of the infection and the treatment approach used.
Q5: What is the survival rate for each condition?
Emphysema survival rate is based on disease stage and treatment but remains constant with good care. Empyema is very treatable if diagnosed early but becomes riskier in advanced stages.
Reference links:
https://www.scribd.com/presentation/164871841/Emphysema-Empyema
https://wikidiff.com/empyema/emphysema
Disclaimer: The content shared on this page is for informational purposes and not for promotional use.